SoFA Urban Garden
Located at 490 South First Street
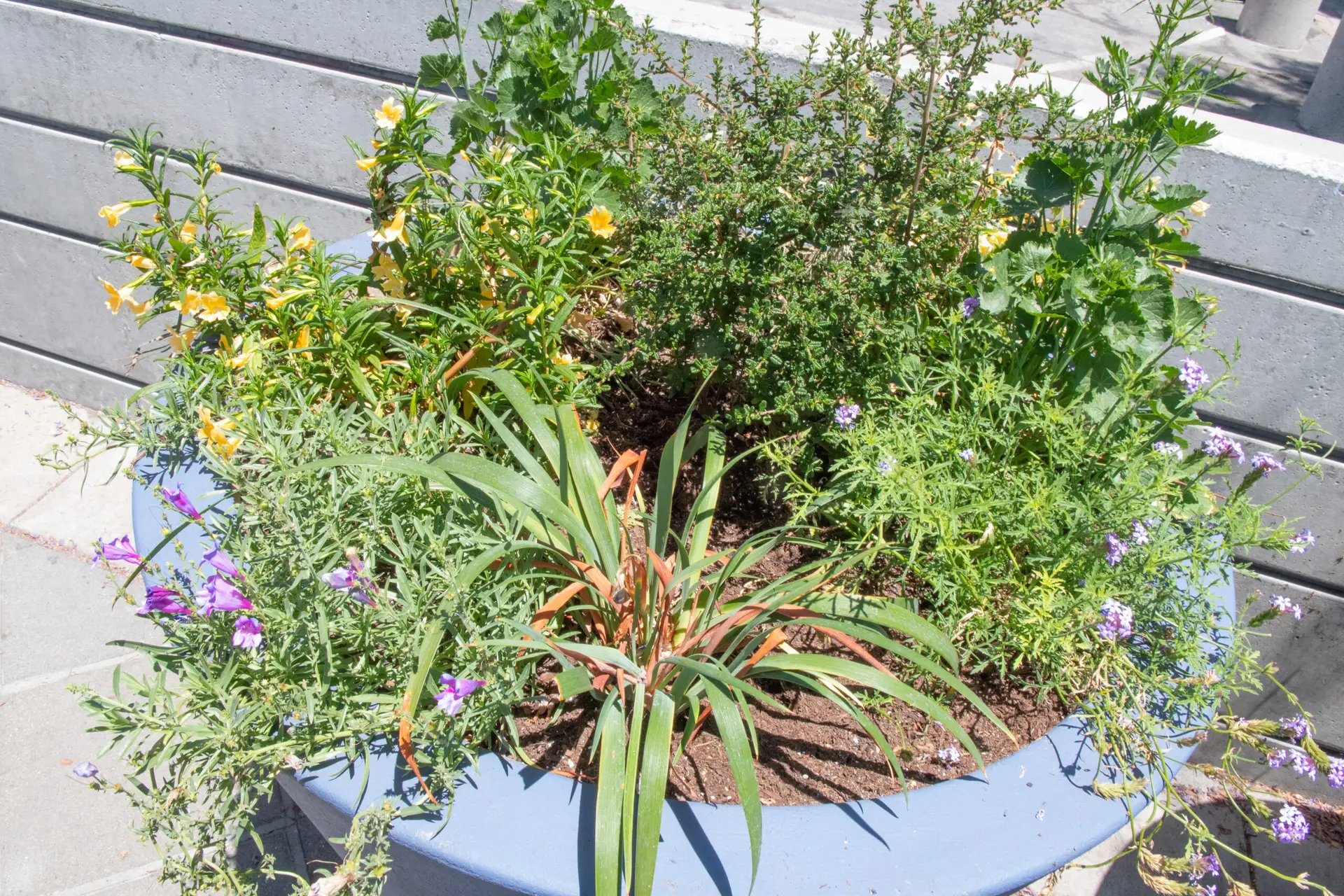
California grassland
Dark Star Ceanothus
Scientific Name: Ceanothus 'Dark Star'
Native Habitat: A hybrid between Santa Barbara Ceanothus and Wartleaf Ceanothus, two native plants that are only found in Central California coastal mountain ranges
Dark Star Ceanothus produces a dark blue flower during the winter that also carries a fragrant scent. In the wild, this plant is very bushy, and is great habitat for pollinators and quail.
Monkey Flower
Scientific Name: Mimulus aurantiacus
Native Habitat: Western North America from Alaska to California and Colorado. Can be found at streambanks 4,000 to 10,000 ft above sea level.
This flower is an important flower for pollinators in the Sierra Nevadas. It prefers rich soil and is a common flower to use in pollinator gardens.
Cedros Island Verbena
Scientific Name: Verbena lilacina ‘de la Mina’
Native Habitat: Native to Cedros Island and the Baja California coast. Although the plant is native to Baja California, it is still part of the California Floristic Province, which is a Mediterranean-climate region from Oregon to Baja California.
Cedros Island Verbena is a butterfly favorite and its purple star shaped flowers bloom throughout the year. This verbena variety, ‘de la Mina’, was selected from the Santa Barbara Botanic Gardens, and has great use in a variety of gardens.
Douglas Iris
Scientific Name: Iris douglasiana
Native Habitat: Coastal regions of southern Oregon and northern California.
The Douglas Iris is a common flowering perennial herb that comes in multiple colors between purple and white. It is often used as ground cover in landscaping, and is also deer-resistant due to its bitter taste.
Foothill Penstemon
Scientific Name: Penstemon heterophyllus
Native Habitat: Found only in California in coastal and northern Sierra ranges.
The Foothill Penstemon is a shrub found in multiple ecosystems ranging from grassland, chaparral, woodland, and forest. It produces clusters of tubular flowers that come in blue, purple, or magenta colors. The flowers attract a wide variety of pollinators, especially bees and bloom in the winter, spring and summer.
Checkerbloom
Scientific Name: Sidalcea malviflora
Native Habitat: Found in dry open areas throughout California.
Checkerbloom is a common herb that produces pink flowers during the spring and summer. In landscaping, it is used as groundcover and as a pollinator plant.

California Poppy
Scientific Name: Eschscholzia californica
Native Habitat: Includes California and extends to Oregon, Washington, Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico, Sonora and northwest Baja California
The California Poppy is an iconic flower in the American West. It became California’s state flower in 1903, and its image can be found here in SoFA District on the California Theater’s light sign. California poppies bloom between February and September, and its flowers only open during the day time. At night or during cold weather, the flowers close up. California poppies are also drought tolerant, self seeding, and easy to cultivate in any garden.
Douglas Iris
Scientific Name: Iris douglasiana
Native Habitat: Coastal regions of southern Oregon and northern California
The Douglas Iris is a common flowering perennial herb that comes in multiple colors between purple and white. It is often used as ground cover in landscaping, and is also deer-resistant due to its bitter taste.
Foothill Sedge
Scientific Name: Carex tumulicola
Native Habitat: Primarily on the coasts of northern California, but extends to San Luis Obispo County and the Channel Islands.
The Foothill Sedge is a grass-like herb that grows in meadows and open woodlands between sea level and 4,000 ft. It prefers open spaces with some moisture, but can tolerate dry periods. For gardening, Foothill Sedge is commonly used as ground cover between trees and shrubs, and is fairly low maintenance.
Monkey Flower
Scientific Name: Mimulus aurantiacus
Native Habitat: Western North America from Alaska to California and Colorado. Can be found at streambanks 4,000 to 10,000 ft above sea level.
This flower is an important flower for pollinators in the Sierra Nevadas. It prefers rich soil and is a common flower to use in pollinator gardens.
Blue Eyed Grass
Scientific Name: Sisyrinchium bellum
Native Habitat: Found throughout California in grassy areas and woodlands.
Blue Eyed Grass is a flowering herb that is easy to grow. It produces small blue and purple flowers that die during the summer. The plant then reseeds itself after its dormancy.
Cedros Island Verbena
Scientific Name: Verbena lilacina ‘de la Mina’
Native Habitat: Native to Cedros Island and the Baja California coast. Although the plant is native to Baja California, it is still part of the California Floristic Province, which is a Mediterranean-climate region from Oregon to Baja California.
Cedros Island Verbena is a butterfly favorite and its purple star shaped flowers bloom throughout the year. This verbena variety, ‘de la Mina’, was selected from the Santa Barbara Botanic Gardens, and has great use in a variety of gardens.
Checkerbloom
Scientific Name: Sidalcea malviflora
Native Habitat: Found in dry open areas throughout California.
Checkerbloom is a common herb that produces pink flowers during the spring and summer. In landscaping, it is used as groundcover and as a pollinator plant.
Planter Themes
Redwood Forest
California Wetland
Oak Woodland
California Chaparral
California Grassland
Coastal Sage Scrub
DID YOU ENJOY THIS EXPERIENCE?
Let us know in this survey
HOW ARE THE PLANTS DOING?
Submit a maintenance request









 Downtown just got tastier! The Pressroom
Downtown just got tastier! The Pressroom

 BIG ANNOUNCEMENT
BIG ANNOUNCEMENT




